What is Welding? A Journey Through Its Evolution, Techniques, and Impact

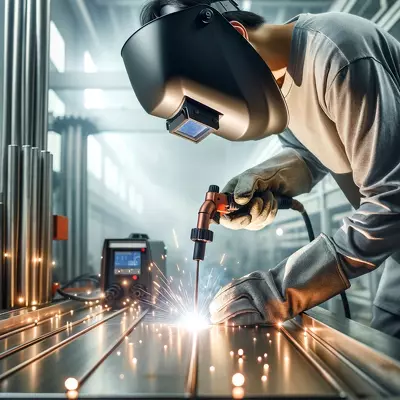
Ever noticed how bridges, cars, and even your bicycle are held together? Welding is the secret behind these strong connections, crucial in constructing and maintaining our metal-made world. Welding involves more than just melting metals together; it’s an essential skill that shapes structures and tools we use every day, employing techniques to create incredibly strong joints. Dive into this article to explore the fundamental principles and mechanical insights of welding and understand why this technique is indispensable across various industries.
I. Introduction to Welding
A. Definition and Basic Understanding
Welding is a fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to form a strong joint. This technique is fundamental in creating everything from household items to large-scale structural frames.
B. Historical Background of Welding Techniques
Welding has been around since ancient times, beginning with rudimentary methods such as forge welding, where blacksmiths joined iron and steel by heating and hammering. The 19th and 20th centuries saw major advances with the introduction of arc welding and oxy-fuel welding, revolutionizing construction and manufacturing industries by providing stronger and more reliable joints.
C. Importance of Welding in Modern Construction and Manufacturing
In contemporary settings, welding is indispensable in constructing buildings, bridges, ships, and automobiles. Its ability to provide durable and robust joints capable of withstanding high stresses and adverse environmental conditions makes it a pillar of modern manufacturing and construction industries.
II. The Fundamentals of Welding
A. Different Welding Processes Explained
Several welding processes exist, each suitable for different applications and materials. Common methods include MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and Stick welding. Each has specific advantages depending on the materials involved and the desired strength of the weld.
B. The Role of Heat and Metals in Welding
Welding typically involves the application of heat to melt the base materials along with a filler metal to form a strong, cohesive bond. The choice of metal and the heat source can vary widely, influencing the quality and attributes of the final weld.
C. Common Tools and Equipment Used in Welding
The equipment used in welding varies from simple handheld tools to complex automated systems. Essential welding gear includes welding torches, electrodes, helmets, and protective clothing, all designed to ensure that welding is performed safely and effectively. Additionally, welding machines play a crucial role, providing the necessary power and precision for various welding tasks.
III. Applications of Welding
A. Welding in Industrial Settings
Industrial applications of welding are vast and vital. In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, welding is crucial for assembling everything from precision components to large structural segments.
B. Everyday Applications of Welding
Beyond industrial use, welding is key in creating art sculptures, jewelry, and home repairs. It allows both professionals and hobbyists to fabricate and repair metal items easily.
C. Innovative Uses of Welding in Advanced Projects
Advancements in welding technology have opened up possibilities for more complex and refined projects, such as underwater welding and space structures, expanding the boundaries of what can be built and repaired.
IV. Understanding Welding Safety
A. Safety Gear and Best Practices
Protective clothing, helmets, gloves, and goggles are essential to shield welders from the intense heat, sparks, and potentially harmful radiation produced during welding. Adhering to safety best practices minimizes risks and ensures the well-being of the welder.
B. Common Risks Associated with Welding
Welding poses several risks, including burns, eye damage, inhalation of toxic fumes, and electric shock. Awareness and proper safety measures are crucial to prevent these hazards.
C. Preventative Measures and Safety Protocols
Implementing rigorous safety protocols such as proper ventilation, regular equipment checks, and safety training can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries in welding operations.
V. FAQs
Q: What is the most common type of welding for beginners?
A: MIG welding is generally recommended for beginners due to its simplicity and versatility.
Q: Can welding be performed on all types of metals?
A: Most metals are weldable, but some, like aluminum and stainless steel, require specific techniques and equipment.
Q: Is it expensive to start welding?
A: Initial costs can vary, but basic welding equipment suitable for small projects can be relatively affordable.
Q: How long does it take to learn welding?
A: Basic welding skills can be learned in a few weeks, but mastering different techniques may take years of practice.
Q: Can welding be self-taught?
A: Yes, with access to the right resources and tools, individuals can teach themselves basic welding techniques.
Q: Are there any health risks associated with welding?
A: Yes, without proper precautions, welding can pose health risks, such as exposure to harmful fumes and ultraviolet radiation.
Q: What advances in welding technology are most significant?
A: Recent advances include ultrasonic welding and laser welding technologies, which allow for stronger welds and greater control.
VI. Conclusion
A. The Future of Welding
The future of welding holds promising advancements in automation and new materials, which are set to enhance efficiency and possibilities in the welding industry.
B. How Welding Continues to Shape Industries
As technological and material innovations continue, welding will remain a crucial skill in manufacturing and construction, contributing to the development of safer, more efficient structures.
VII. Suggested Readings
Welding offers a fascinating window into the world of industrial arts and practical engineering. Whether you are a professional looking to refine your skills or a hobbyist starting, these books provide invaluable insights:
- “Modern Welding Technology” by Howard B. Cary – This book provides detailed coverage of the latest equipment and techniques in welding.
- “Welding: Principles and Applications” by Larry Jeffus – A comprehensive guide that explains both fundamental and advanced welding applications.
- “The Welding Business Owner’s Handbook” by David Zielinski – Offers advice on starting and operating a profitable welding business.
- “Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels” by John C. Lippold and Damian J. Kotecki – Delves into the properties of stainless steel and its challenges in welding.
Understanding welding through these readings can deepen your appreciation of this essential craft and open up new avenues for personal and professional growth.