MIG Welding with Argon Gas: Cleaner Welds and Greater Control

Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases—at no extra cost to you.
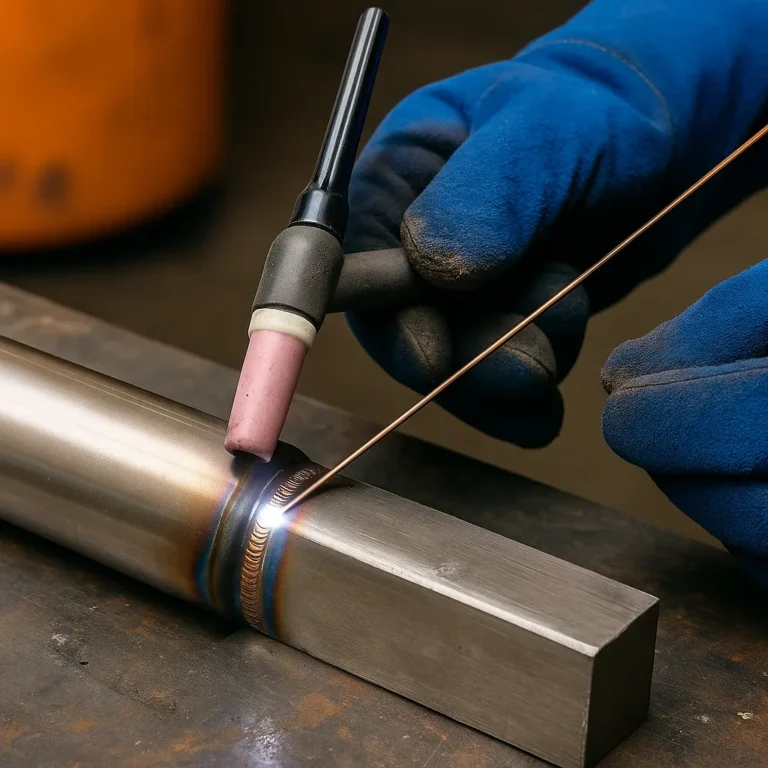
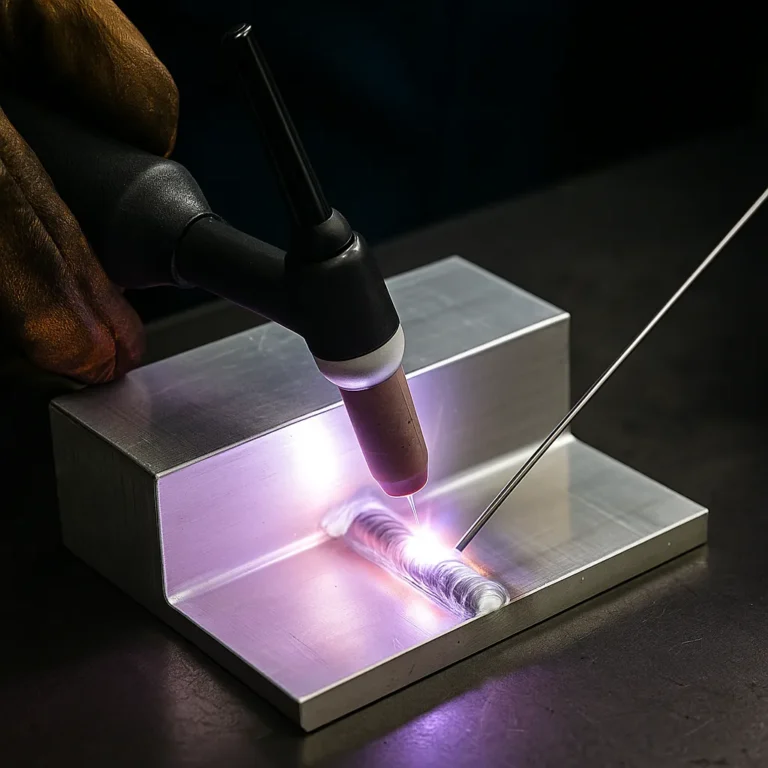
MIG welding is a go-to technique for fabricators, mechanics, and metalworkers, and the type of shielding gas used can significantly affect your weld quality. Among the various options, argon gas stands out for its clean, stable arc and precise control. While it’s not always the only gas used in MIG welding, it plays a crucial role—especially when working with non-ferrous metals like aluminum and stainless steel. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about MIG welding with argon gas.
Why Argon Matters in MIG Welding
Argon is a colorless, odorless, and inert gas, which means it doesn’t chemically react with molten metal. This makes it an ideal shielding gas for MIG welding, as it protects the weld pool from contaminants in the air such as oxygen and nitrogen. Without proper shielding, welds can become porous, weak, or heavily oxidized.
Argon helps create a narrow, focused arc that gives welders better control, especially on thinner metals or detailed work. However, it’s essential to understand when to use pure argon and when to blend it with other gases for optimal results.
When to Use Pure Argon in MIG Welding
Pure argon is typically used in MIG welding when working with non-ferrous metals like:
- Aluminum
- Magnesium
- Titanium
For aluminum in particular, pure argon provides the cleanest arc start and smoothest bead. It also reduces spatter and helps produce the aesthetically pleasing welds often required in automotive, aerospace, or decorative metalwork.
However, argon alone has limited penetration in ferrous metals like steel. That’s why welders rarely use pure argon for mild steel—doing so can result in weak welds and incomplete fusion.
Argon Gas Mixtures for Steel Welding
When it comes to welding carbon or stainless steel, argon is usually mixed with other gases to improve weld performance. Common blends include:
- 75% Argon / 25% CO₂ (C25): This is the most widely used mixture for general steel welding. It balances arc stability, penetration, and minimal spatter.
- 90% Argon / 10% CO₂: Ideal for spray transfer welding techniques on thicker metals.
- 98% Argon / 2% Oxygen: This is used for stainless steel and provides a smooth, stable arc with low oxidation.
These blends make use of argon’s arc control while adding elements that enhance penetration and fusion for steel projects.
Benefits of MIG Welding with Argon
- Stable arc: Argon ensures a smooth, controlled arc that’s easy to manage for all skill levels.
- Reduced spatter: Especially with pure argon or argon-rich mixes, you get a cleaner working environment and less post-weld cleanup.
- Better bead appearance: Argon helps create a shiny, consistent weld bead that’s visually appealing.
- Lower oxidation: By displacing atmospheric gases, argon protects the weld from contamination.
Conclusion
MIG welding with argon gas provides superior arc control, cleaner results, and less spatter—especially when working with aluminum or using argon-rich blends for steel. Whether you’re a beginner or seasoned welder, understanding how to use argon effectively will improve the quality and appearance of your welds. Choose the right gas mix for your base metal, and let argon help you weld like a pro.